Selective laser sintering (SLS)
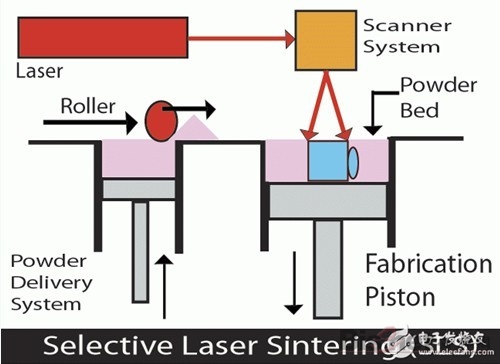
Digital model layered cutting and layer-by-layer manufacturing are the basis of the 3D printing process, and will not be repeated here. In addition, the SLS process is similar to the SLA light curing process, which requires the use of laser to cure the material into a whole. The difference is that the SLS process uses an infrared laser beam, and the material is changed from photosensitive resin to powder of plastic, wax, ceramics, metal or its composite.
First, a very thin layer (sub-millimeter level) of raw material powder is not spread on the table, and then the laser beam under the control of the computer is scanned by the scanner at a certain speed and energy density according to the two-dimensional data of the layer. The powder scanned by the laser is sintered into a solid layer with a certain thickness, and the unscanned area still remains loose powder.
After the first layer is scanned, the next layer is scanned. First lift the worktable according to the thickness of the cut layer of the object, the powder spreading roller will flatten the powder again, and then start the scanning of a new layer. This is repeated until all levels have been scanned. Remove the excess powder, and then after proper post-processing such as grinding and drying, you can obtain parts.
At present, when this process is applied, wax powder and plastic powder are used as raw materials, and the process of bonding or sintering with metal powder or ceramic powder has not yet been actually applied.
Laminated object manufacturing (LOM)
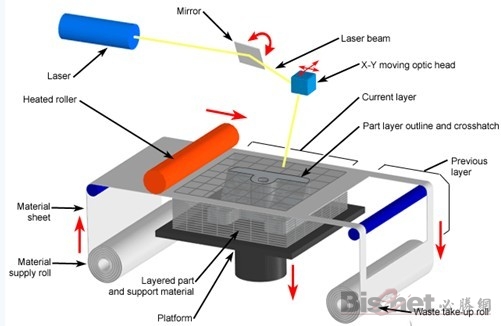
In the lamination stack manufacturing process, the machine will heat the foil coated with hot sol on one side by a hot roller. The hot sol can be sticky when heated, so materials composed of paper, ceramic foil, metal foil, etc. Glued together. Next, the upper laser layered the data according to the CAD model, and the laser beam was used to cut the foil into the inner and outer contours of the manufactured parts. Then lay a new layer of foil, bond it with the cut layer under the hot pressing device, and the laser beam cuts again. Then repeat this process until the entire part is printed.
It is not difficult to find that the LOM process still has the shadow of traditional cutting. It's just that instead of using bulk raw materials for overall cutting, it divides the original part model into multiple layers and then performs layer-by-layer cutting. The 3D printer originally developed by the Beijing Taier era is also a 3D printer of the LOM process. However, because it uses paper as a raw material, laser cutting has the risk of ignition, and the application is limited, so the Taier era later turned to the FDM process.
Three-dimensional printing process (3D printing, 3DP)
Three-dimensional printing, also known as three-dimensional printing. Wikipedia shows that in 1989, MIT's Emanuel M. Sachs and John S. Haggerty applied for a patent for the 3D printing technology in the United States, and then Emanuel M. Sachs and John S. Haggerty improved the technology many times. And finally formed today's three-dimensional printing process.
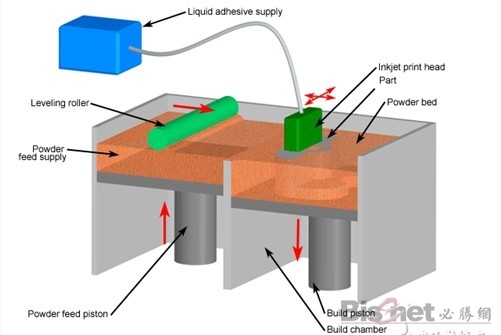
In terms of working methods, 3D printing is the closest to traditional 2D inkjet printing. Like the SLS process, 3DP also makes parts by bonding the powder as a whole, the difference is that it is not bonded by laser melting, but by the adhesive sprayed from the nozzle.
Under the control of the computer, the spray head runs according to the two-dimensional data of the model cross section, selectively sprays the adhesive at the corresponding position, and finally forms a layer. After the bonding of each layer, the forming cylinder drops by a distance equal to the thickness of the layer, and the powder supply cylinder rises a certain height to push out the excess powder, which is pushed by the powder spreading roller to the forming cylinder, flattened and compacted. This cycle until the entire object is bonded.
The device on the front is ZPrinter, a 3DP printer in use by Suntop Technology.
Organ package, also called transaction package, is a kind of document package that is often used in business and office.Because of its internal partition, pull open the same as the organ, so named for the organ package.The organ bag has various materials and sizes, which can be used to store all kinds of office documents in daily office, which is convenient to carry and easy to save.The PP organ bag produced by our company is made of high quality environmental protection and durable PP raw material. Generally, a transparent name card bag is pressed on the front, and the button switch or hand carry is provided for easy carrying.
Expanding Folders,Expanding File Folder,Pp Expanding File Folder,Custom Expanding Folders
shaoxing chaofeng stationery manufacturing CO.,LTD. , https://www.chaofengstationery.com